Uveitis
Your guide to management and treatment.
What is Uveitis?
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, or the middle layer of tissue in the eye that includes the iris, ciliary body and choroid. It affects everyone differently; some people have mild symptoms and slightly reduced vision, and others experience debilitating symptoms and severe, permanent vision loss.
Conditions like uveitis should be managed and treated by eye care professionals like the team at The Eye Health Centre. Our retinal specialists understand what causes uveitis and are very knowledgeable about solutions to fight inflammation, prevent further damage and restore loss of vision.
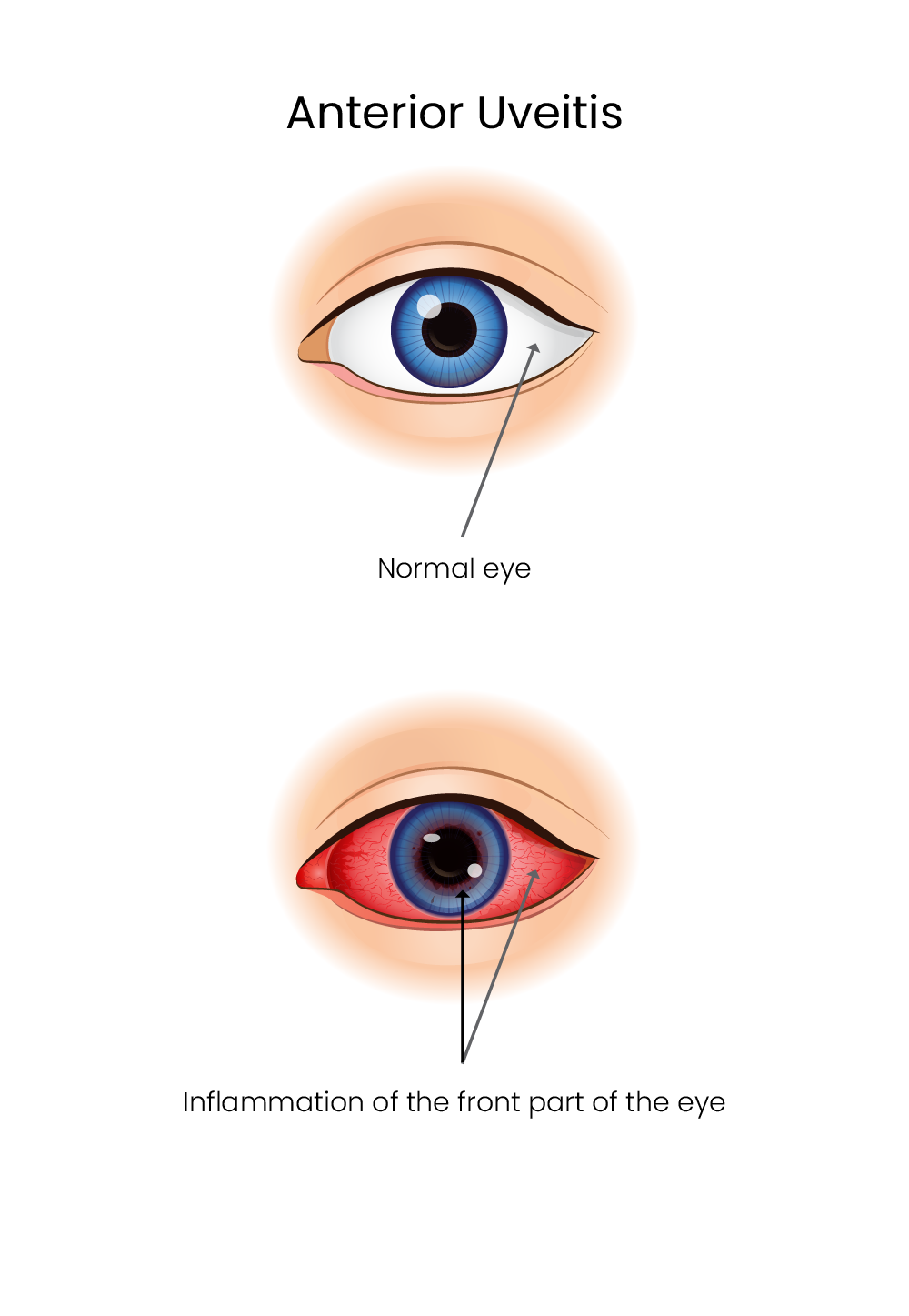
What are the symptoms of Uveitis?
Uveitis can cause eye redness, pain, blurry vision, sensitivity to light and floaters. The onset of symptoms may be sudden or gradual, and they can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may be chronic or intermittent (e.g., occasionally getting better and then worsening). Every so often, there are no noticeable symptoms of uveitis and the condition is only detected through a routine eye exam.
If you experience any changes in vision or eye pain, you should promptly see our eye doctors for an evaluation.
What causes Uveitis?
Uveitis may be caused by an infection, tumor, eye injury or an autoimmune or inflammatory disorder that affects other parts of the body (e.g., Crohn’s disease, lupus, sarcoidosis). In some cases of uveitis, there is no identifiable cause.
There are four types of uveitis, each characterized by the specific part of the eye affected.
- Anterior uveitis: Affects the front part of the eye, between the cornea and the iris. It is the most common form of the disease.
- Intermediate uveitis: Affects the retina, vitreous (gel-like substance in the center of the eye) and the pars plana (blood vessels behind the lens). It often occurs in young adults.
- Posterior uveitis: Affects the retina or the choroid on the inside back of the eye. It is the least common form of the disease.
- Panuveitis: Affects all layers of the uvea.
Panuveitis, intermediate and posterior uveitis are the most likely to cause blindness if they go untreated.
How do we diagnose Uveitis?
To diagnose uveitis, our doctors will perform a comprehensive eye exam and take down your complete health history. During the exam, the doctor will assess your vision and evaluate the front and back of your eye. Additionally, the doctor may check your intraocular pressure. The exam is completely non-invasive and you should not feel any discomfort.
Depending on the findings of the exam, the doctor may order additional tests. If an underlying systemic health condition is believed to cause your uveitis, you may need to see your primary care physician for lab testing.
How do we treat Uveitis?
Treatment for uveitis depends on the type and cause. In cases that are linked to an underlying health condition, treating that specific condition can improve the inflammation in the eye.
Treatment solutions for uveitis include eyedrops to reduce inflammation in the eye, drugs to treat bacterial or viral infections or drugs to suppress the immune system.
Serious cases of uveitis that do not respond to medical treatment may require vitrectomy surgery or the placement of an eye implant that slowly releases medication over a prolonged period of time.
Do you have a question or concern about your eye health? To discuss your condition with an experienced ophthalmologist or optometrist, please contact The Eye Health Centre

